The Nuclear Power Plant | The Nuclear Power Plant Definition & Diagrams
Table Of Interest
Today, you and I will quickly take a look at the topic “The Nuclear Power Plant | The Nuclear Power Plant Definition & Diagrams”.
This has become necessary as we have sen overtime that several individuals have been searching for topics related to the above topic The Nuclear Power Plant | The Nuclear Power Plant Definition & Diagrams.
However, if you are among those that have been searching for answers to [nuclear power plant working, nuclear power plant diagram, list of nuclear power plants, nuclear power plant india, nuclear power plant definition, nuclear power plant pdf, nuclear power plant advantages and disadvantages, nuclear power plant ppt, The Nuclear Power Plant | The Nuclear Power Plant Definition & Diagrams], then you can see that you are not the only one.
Nonetheless, you shall get all this information right here on this blog.
The Nuclear Power Plant | The Nuclear Power Plant Definition & Diagrams
we may wonder at times or rather thought of what nuclear power plant is all about, this post is basically about the working principle behind nuclear power plant.
Most time if the word NUCLEAR is spoken we immediately think of weapons of mass destruction but moreover nuclear physics is of more good to us than its disadvantage meanwhile if used meticulously and wisely.
Nuclear power plant is simply converting the mass heat energy from its fission or fusion ( like combustion ) to other forms of useful energy.
Hence fission and fusion is simply a nuclear chemical process that produces large amount of heat energy up to that of the sun core, in fact the sun uses nuclear processes in producing its heat, and also how the conversion of energy is being done, all of these would be treated below.
WHAT IS A NUCLEAR REACTION
In physic or rather in nuclear science in general, nuclear reaction is that reaction that involves a nucleus of an atom or most times two nucleus of an atom or even its sub atomic particle like proton, neutron or high velocity electron.
The reaction occurs when these particles collides together or split to form other nucleus or nuclei which are different from the once at the initial stage, In nuclear reaction there is always a transformation of at least one nucleus or any of it sub atomic particles.
Moreover nuclear scattering is often different from nuclear reaction in that it is simply the reaction that involves an unchanged nucleus but great energy is give away by heat and light. in general, in nuclear reaction a huge amount of energy is given out as heat and light.
Basically there are two types of nuclear reaction:
•nuclear fission: in this process atoms, its nucleus or even its sub atomic particles splits to for other nucleus or particles which are lighter than its parent atoms, It can be a radioactive decay or a nuclear reaction. A good example of such reaction is Uranium-236 nucleus splits to form krypton-92 and Barium-141.
•nuclear fusion: this involves two or more nucleus or subatomic particle coming together or rather collides to form a single nuclei or subatomic particles which is more heavier than its parent atom. A good example is two hydrogen atom or nucleus coming together to form helium particle. This reaction occurs in the sun and is responsible for the huge amount of heat and light given off.
Generally nuclear reaction are normally chain reaction in that it continues to occur to every particle involve and the particles given off serves as a trigger to other reactions to occur, it then turns to a continuous reaction and if not controlled.
NUCLEAR POWER PLANT
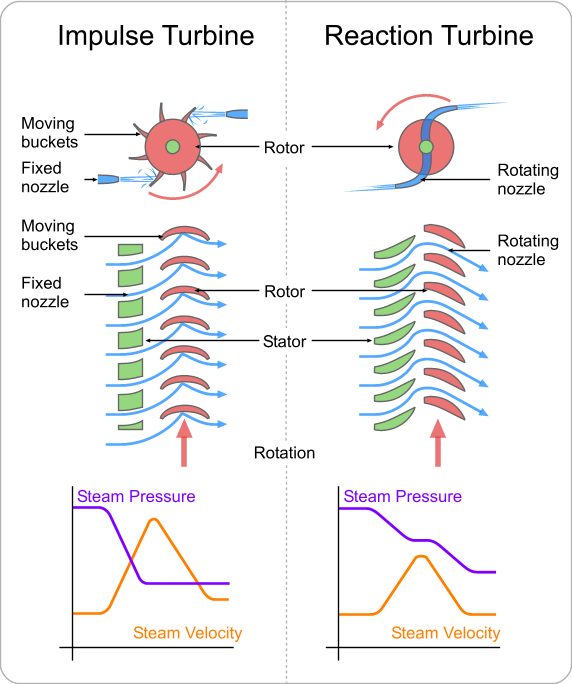
Engineers of the 19th century have tried to harness the energy from heat and many equipment have been made but one of them of them stands of more significant and economical, it is known as a turbine; it is a simple series of blade connected to a shaft meanwhile the blade uses kinetic energy from fluid flow to drive the shaft.
It is a simple mechanical device that converts energy from fluid flow to useful work.
Moreover this fluid that drives this turbine is need to be of high velocity or speed and thinking of it the only way a fluid can be of high velocity is when it is pressurized, the better and cheaper way of pressurizing a fluid is by heating it in a confined container.
Most times this fluid is water pressurized to steam.
The question now is how is the water going to be heated to steam?, before the evolution of nuclear physics burning of coal where used and later on gases or other fuel which are in limited supply.
In modern days controlled nuclear reaction is being used and the heat energy is harness to heat the fluid to be pressurized, more over since nuclear reactions produces huge amount of heat and it is also radioactive it is done in a confined space or container called nuclear reactor.
In the NUCLEAR POWER PLANT the turbine which converts fluid energy to useful work is used to drive a Generator which converts the immediate energy to electrical energy and it is transmitted through the power grid to its consumers.
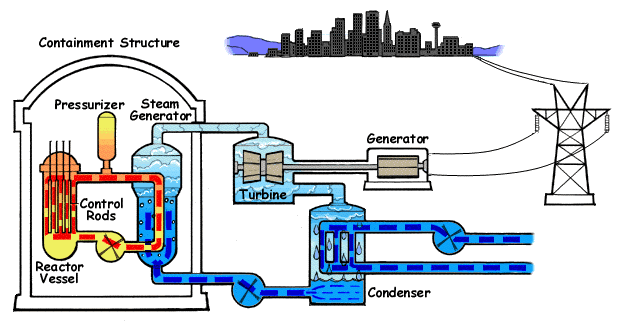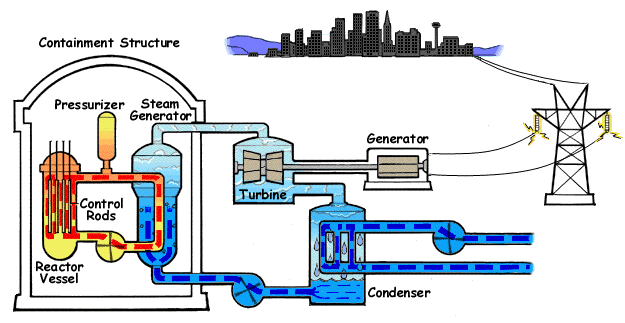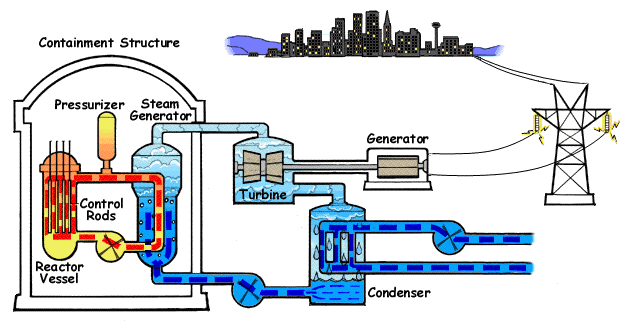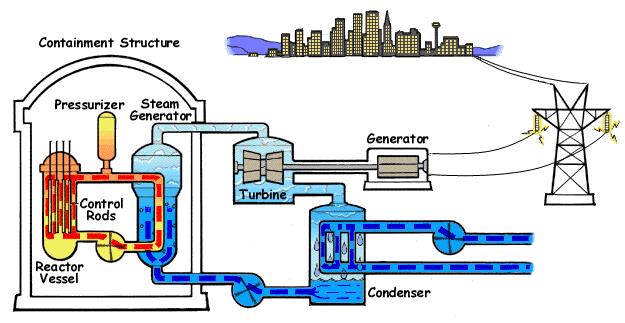
MAJOR PARTS OF THE NUCLEAR POWER PLANT
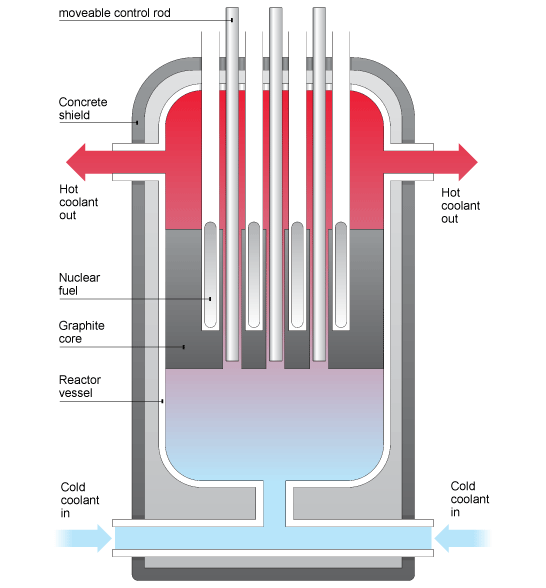
▪Nuclear Reactor: This is the most essential part of the plant due to the fact that energy is generated here, it is known as the heart of the plant as the neccessary heat is produced by nuclear fission as it is used to raised steam which runs through a turbine.
Hence useful work is done and may be used to drive and secondary machine (generator).
the fuel used for this nuclear chain reaction is usually uranium which kinda abundant in earth. usually the heavy metal ‘uranium’ comes in different isotopes which are uranium-238 (U-238), accounting for 99.3% and uranium-235 (U-235) accounting for about 0.7%.
They have different rate of chain reaction.
Moreover due to the fact that nuclear fission occur with a high amount of radioactivity, the core is made of protective sheild which absorbs radiation and protects the radioactive waste to go into the atmosphere.
See Other Articles Others Are Reading
- History As A Science | What Makes History A Science
- Fire And Safety | Basic Fire Safety Tips & Fire Safety Rules
- Myths Surrounding Exercises | All You Need To Know Concerning Exercises.
- Criminal Profiling – Facts Over Fiction | Criminal Profiling Techniques
- 5 Tips For Students Who Are Considering Graphic Design As A Career.
- Evaluation Of Learning: How To Know If The Children Are Learning
Also in chain reaction moderators are used to slow down the nuclear reaction examples of moderators are graphite rods.
▪Steam Turbine: As said early, a turbine is a mechanical device that convert fluid work to useful mechanical work.
It is the primary stage devices for conversion of energy.
Basically the Steam turbine house is usually separated from the reactor struction this is due to the fact that when ever there is complications in the turbine house it does not extend to the nuclear reactor thus minimizing risk for nuclear accident.
In most power plant an intermediate heat exchanger is placed in between two fluid flowing process, the first fluid is heated directly by the nuclear reactor hence it known to have traces of radioactive materials and the other flows to the turbine, this is done to minimize radioactive substance from entry the atmosphere.
Also an activity meter is mounted to track the outlet steam of the steam generator for safety purpose
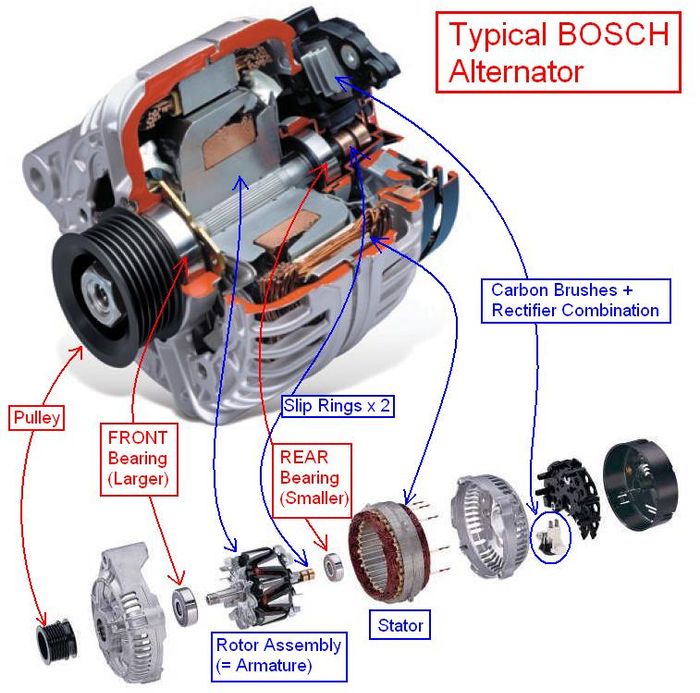
▪Generator: A generator also known as a alternator is an electrical device that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy, it is a rotary machine that uses the useful work in the turbine to produce electricity.
Basically a Low-pole AC synchronous generators of high rated power are used. These alternators may be connected in series or parallel depending on the purpose of the plant.
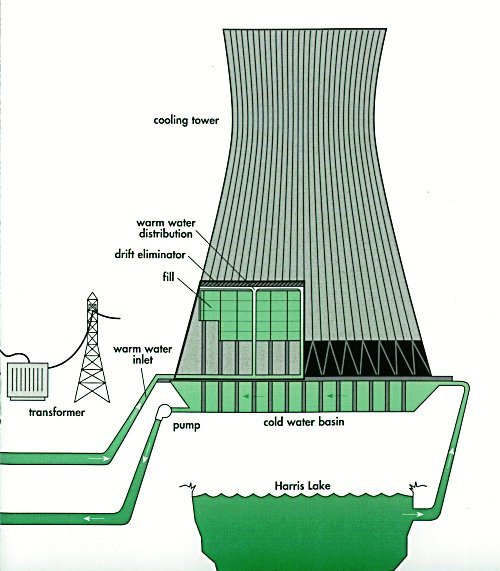
▪The Cooling Tower: This is the part seperating the nuclear reactor and the turbine house, its the system that cools the reactor moreover the heat harnessed for the cooling system is used to drive one or mor turbines which drives the generator.
Most time an intermediate heat exchanger is placed in between two fluid flow to minimize radiation.
The minor parts of a nuclear power plant includes the safty valves which is employed when there is an uncontrollable fluid pressure in pipes and prevents the pipe and essential equipment from bursting, The Main Condenser; it is located at the exhaust part of the plant, it turns a saturated steam back to water by asborbing it heats it works with the principle of heat exchanger.
The feed pumps these are mechanical devices that works with the principal of compressors, their main function is to bring water or steam at low pressure to a state of high pressure. it can be concluded that it pressurizes fluids.
This post shows the brief explanation behind the working principle of a nuclear power plant and as cheap source of power supply with respect to a large scale production.
That’s the much we can take on the topic “The Nuclear Power Plant | The Nuclear Power Plant Definition & Diagrams”.
Thanks For Reading
See Other Articles Others Are Reading
- History As A Science | What Makes History A Science
- Fire And Safety | Basic Fire Safety Tips & Fire Safety Rules
- Myths Surrounding Exercises | All You Need To Know Concerning Exercises.
- Criminal Profiling – Facts Over Fiction | Criminal Profiling Techniques
- 5 Tips For Students Who Are Considering Graphic Design As A Career.
- Evaluation Of Learning: How To Know If The Children Are Learning

Leave a Reply