Missile Technology – The Weapon Of Destruction
Table of Interests
Today, you and I will quickly take a look at the topic “Missile Technology – The Weapon Of Destruction“.
This has become necessary as we have sen overtime that several individuals have been searching for topics related to the above topic Missile Technology – The Weapon Of Destruction.
However, if you are among those that have been searching for answers to [list of weapons of mass destruction, countries with weapons of mass destruction, biological weapons of mass destruction, chemical weapons of mass destruction, effects of weapons of mass destruction, weapons of mass destruction examples, weapons of mass destruction pdf, weapon of mass destruction definition, Missile Technology – The Weapon Of Destruction], then you can see that you are not the only one.

Nonetheless, you shall get all this information right here on this blog.
Missile Technology – The Weapon Of Destruction
The word “Missile” refers to any object which is thrown at a specific target.
In military science missile is defined more precisely as an unmanned vehicle carrying a warhead with certain payloads towards a specific target. Missiles usually carry self-propelling mechanisms to maintain the desired trajectory.
The modern guided missiles are widely used in both in attacking and defense operations across the military universe.
The missile technology is advancing rapidly in recent times as such that Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles (ICBMs) can now engage targets launching from one continent to another.
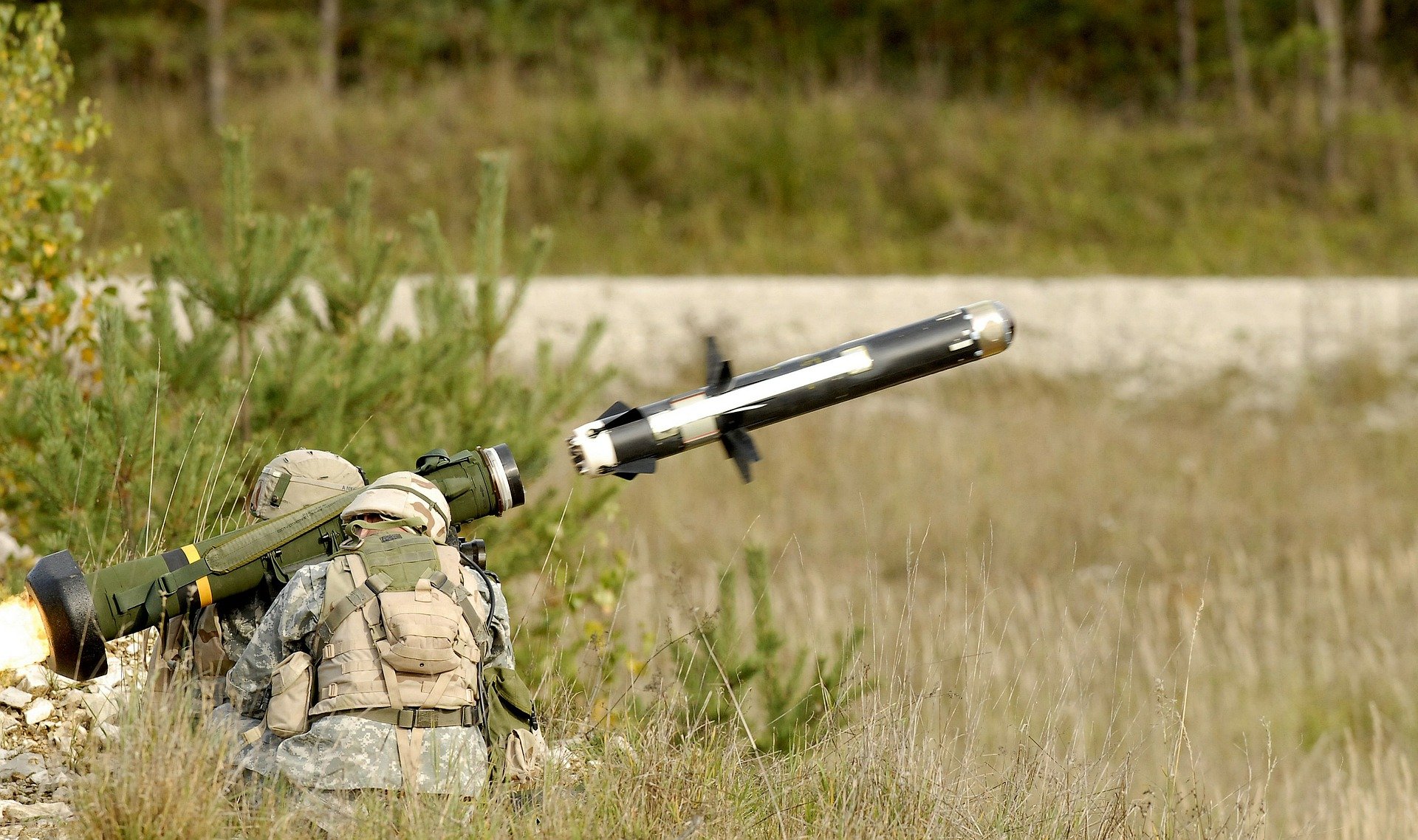

Modern guided missiles are used in a wide range of purposes.
The design and components of the missile depends on the assigned task.
Military agencies across the world use most convenient techniques to design the missile for maximum work ability.
The usage range and strategic divergence of agencies lead to numerous missile structural designs. However, a general overview of missile components can be drawn as followed:
|
|
|
|
Missile Technology – The Weapon Of Destruction | Warhead

The warhead is the core component of a modern missile.
It is responsible for the terminal damage in engagement of a target.
Warheads can carry conventional explosives like TNT which causes fragmentation of metal components in explosion.
Non-conventional missile warheads carries more advanced explosive materials like biological or chemical weapons.
ICMB warheads are designed to carry nuclear weapons for causing mass destruction at the intended target location.
Non-lethal warheads serve the purpose of damaging enemy facilities and disrupt communication.
Warheads often carry multiple sub-munitions that can be deployed from a specific altitude to cover up wide range of target area.
Missile Technology – The Weapon Of Destruction | Airframe

An airframe is the physical structure that bears all other components of the missile.
It also helps to achieve desired aerodynamic characteristics for the flight.
The design of a missile is depended on the operation requirement in general.
Modern military missiles serves a wide range of purpose that lead to a variety of structural design.
Missile airframe is usually a cylinder shaped tube which contains the controlling and propulsion mechanism.
The airframe is equipped with several set of flippers near the center and tail end.
The flippers provide stability and helps the missile to navigate in flight.
The size and number of flippers depend on the task assigned to the missile.
The front end of the air frame carries the warhead of the missile.
Front end design is much dependent on flight speed and desired trajectory of the missile.
For example US Navy’s ‘RIM Terrier’ missile has sharp and slender nose to increase efficiency while traveling in supersonic speed.
the other hand the front end structure of ‘AIM Sidewinder’ missile is hemispherical that supports infrared sensors to receive precise tracking information.
Missile Technology – The Weapon Of Destruction | Propulsion System
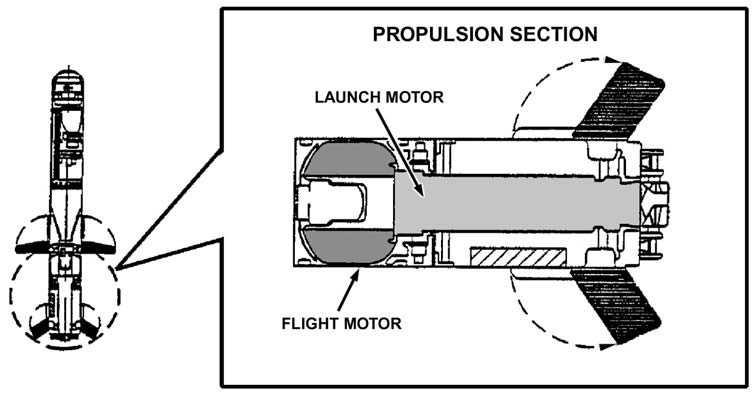
Propulsion system of the missile helps it to acquire the desired thrust and energy to engage with the target.
Most of the modern missiles of today use jet engines as primary population mechanism.
The jet engines operates using the Newton’s 2nd and 3rd law of motion.
The jets receive air from the atmosphere and increase the momentum of the air to gain desired thrust. Exhaust nozzle is attached to the tail of the missile airframe to expel stream of gas in high speed.
Long ranged missile systems like ICBMs use liquid-propellant jet engines as they can maintain high thrust for relatively long period of time. Short & Intermediate range missiles like UGM Polaris, AIM Sidewinder use solid-propellant jet engines for relatively quick launching capability and better fuel reservation range.
Again, the power and range of the jet is determined by the desired requirement of the missile. Supersonic missiles use most advanced and powerful jet engines while short range missile propulsion system comprises of solid jets.
Missile Technology – The Weapon Of Destruction | Control & Guidance System
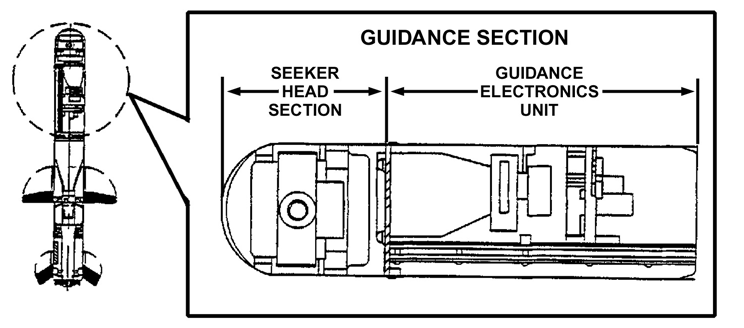
Control & guidance system of a missile works together to keep the missile within desired trajectory. Control & guidance system includes measuring equipment and radio transmission devices.
These systems becomes operational just after the missile leaves the launching pad. Control system also helps the missile to maintain a stable flight within specific trajectory.
The performance of the flippers attached with the airframe is dependent on the command from control mechanism.
The missile propulsion rockets are also guided by these two systems. In terms of long range ballistic missiles, control system determines the jet separation time and initiates the command for the operation.
Missile Technology – The Weapon Of Destruction | Missile Classification
Military agencies across the across the world classify missiles by several means like launch mode, type, range, propulsion and so on. A graphical representation of missile categories are presented in Figure below.
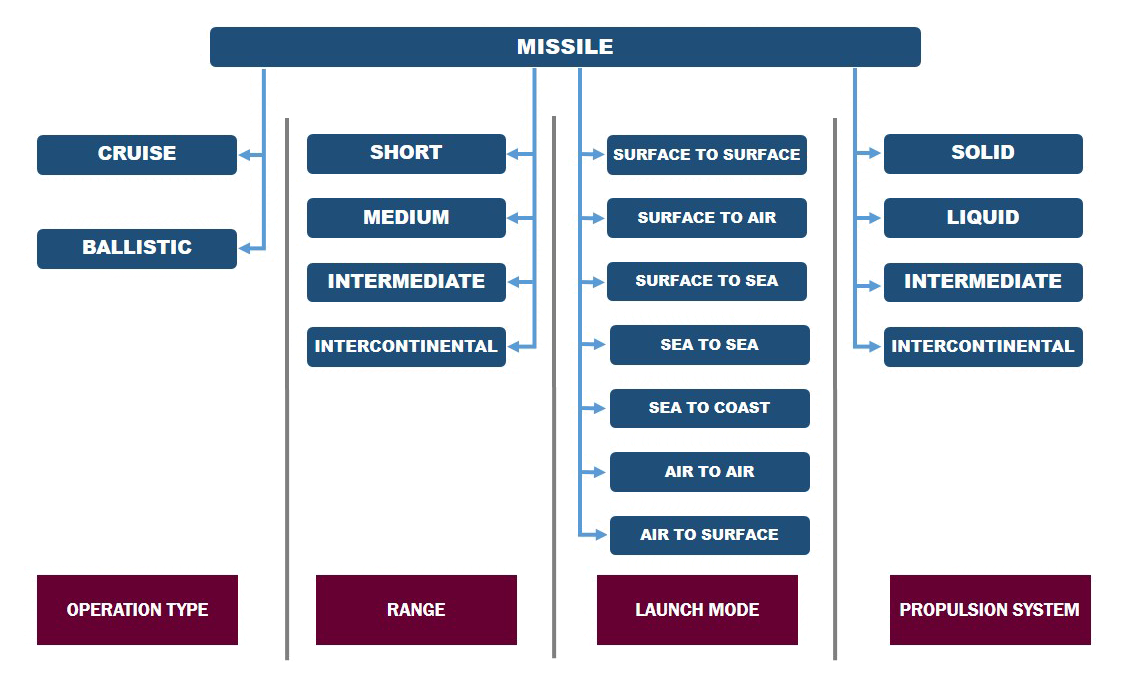
However, the operation principle separates the entire fleet of missile technology into two broad types as Ballistic and Cruise missile. Let’s discuss about the principles and operation of Cruise missiles today.
Cruise missile is a form of self-propelled missile that maintain a constant speed while progressing through the atmosphere.
Cruise missiles are usually used to carry larger payloads towards a specific target.
Cruise missiles are propelled by jet engines throughout the whole course of the flight operation while ballistic missiles experience an unpowered flight at the terminal course of the flight.

The evolution of cruise missiles date back from 1930s to ‘40s.
The first known use of cruise missiles were the V-1 buzz bomb of German Nazi.
Those earlier cruise missiles were charged with electrical fuze and weighted over 1500 lbs.
Since then the cruise missile technology developed towards more lethal and effective operations.
Cruise missiles can be launched from aircrafts, ground vehicles, ships and submarines that makes them suitable for versatile use in military operations.
Depending on the operational strategies, cruise missile can be classified into two types:
- Land Attack Cruise Missile
- Anti-ship Missiles
Missile Technology – The Weapon Of Destruction | Land Attack Cruise Missile
Land Attack Cruise Missiles (LACMs) are designed to combat against land based targets. LACMs provide precise accuracy on hitting a selected target among a group of hostiles.
The V-1 buzz missiles used by German’s in WW2 are the earliest member of LACM category. Modern LACMs can achieve very high operational accuracy that make these cruise missiles feasible in destroying enemy safe houses in civilian locality.
LACMs provides additional flexibility and better accuracy than manned aerial vehicle operations. US Navy and other military agencies used Tomahawk Land Attack Missiles (TLAMs) in Iraq, Libya and Syria wars.
These missiles have been proven to be greatly successful against well defended targets.
This operational success rate made the Tomahawk missiles one of the most famous in recent times. A most recent LACM operation of USS Porter on Syria can be seen from the video below.
Anti-ship Missiles
Anti-ship Missiles (AShMs) are widely used to combat enemy warships around the world.
With the advancement of military technology, warship are developed to launch and upkeep air combats floating on oceans across the globe.
Advanced warships like US Navy’s Nimitz class & Ford class aircraft carriers possess an inordinate threat by supporting both aerial and ground based combat operations. AShMs are designed to counter the defense system of enemy warships beyond their counter-fire range. Like the LACMs, anti-ship missiles were also developed during the WW2 by the Germans.
They used the infamous Henschel Hs-293 to severely damage Allied ships in the Mediterranean Sea. The video shows US submarine named USS Olympia firing an AShM from sinking below the water surface.
Missile Technology – The Weapon Of Destruction | Speed & Trajectory
Modern cruise missiles can reach supersonic speed travelling more than Mach 1 speed.
Military agencies use supersonic cruise missiles to evade Missile Defense System (MDS) and for precise short range operation.
The ongoing research on cruise missile development aims at achieving Mach 6 speed. Hypersonic missiles like ‘X-51 Waverider’ can reach more than Mach 5 speed.
Cruise missiles are capable of operating in multiple atmospheric condition maintaining different flight trajectory. High altitude operations provides longer range but makes the missile vulnerable to enemy air defense.
Anti-ship cruise missiles follows a very lower trajectory altitude to avoid the enemy radar systems.
Modern AShMs like the BrahMos maintains an altitude of few meters above the sea surface while LACMs also maintain lower altitude to avoid detection in general.
Moreover, this low altitude operation is not always preferred because of inefficiency due to the close-surface flight.
Missile Technology – The Weapon Of Destruction | Guidance
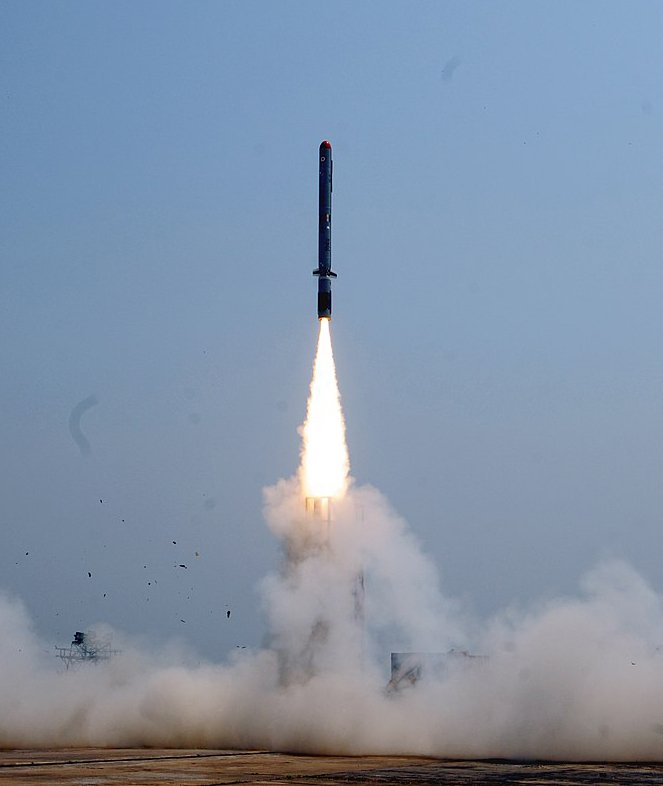

Cruise missiles use multiple guidance system to engage with the target with precise accuracy.
The earlier editions of cruise missiles used inertial guidance system that follows a predetermined flight path. Advanced technologies like laser, GPS and radar guidance are now widely used in modern cruise missiles.
Short range cruise missiles prefer laser guidance mechanism to engage within a group of hostile facilities.
The GPS guided missiles use satellites to maintain desired trajectory and engage the target with increased accuracy.
Both active and passive radars are widely used to navigate cruise missiles to desire trajectory. Terrain Contour Matching (TERCOM) technology is also used in cruise missile guidance.
This navigation system uses the outlined projection of the land to follow the correct flight path using radars mounted on the missile. A TV guidance system operates using a TV camera mounted on the front-end of the missile to guide it to target location manually.
To achieve maximum accuracy in critical target locations, several guidance systems are often used together.
The word ‘missile’ is originated from a Latin word ‘mittere’ which means ‘to send’.
In general, an object which is thrown to a specific target can be called as missile.
So when you throw a stone to a bird or throw a ball at your dog, theoretically you are launching a missile. But the bird may notice your stone and possibly evade by changing its position which makes your missile a complete failure.
To reduce the possibility of failure, you can simply teach your stone to follow the bird wherever it goes.
Well, while you scratch your head wondering ‘how to train your STONE’, military technologists developed their way to follow the moving targets using ‘guided missiles’. The most advanced missile agencies use guided missiles in both defensive and striking operations.

Ballistic Missile
Ballistic Missiles (BMs) are a commonly used unmanned vehicle that carries a warhead to a specific target over a ballistic trajectory. BMs follows a predetermined course of flight and experience unpowered propulsion at the terminal stage of the flight.
These missiles can carry a larger payload to conduct massive destruction. Most advanced ballistic missiles provides the flexibility to operate in longer range.
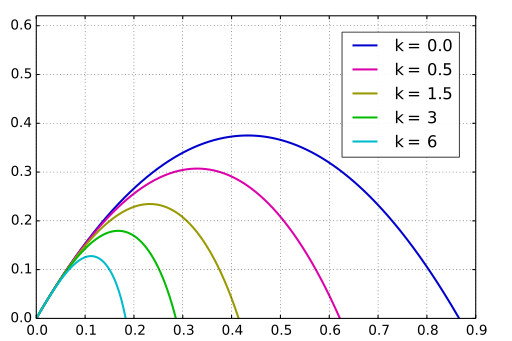
A ballistic trajectory is a flight path of a projectile that is fired in a specific angle (not accurately 90 degree) to reach a certain midpoint and then propelled towards a target using the gravitational force.
The mid-point of a ballistic trajectory is the highest peak of the flight from where object follows the predefined flight path and engage with the target. Sample ballistic trajectories are presented in Figure 2.
Ballistic missiles follow this trajectory to operate effectively against targets in longer distance.
Following this trajectory allows the BMs to maintain the unpowered flight during half of the flight path that in terms increase the operational range of the missile by a significant value.
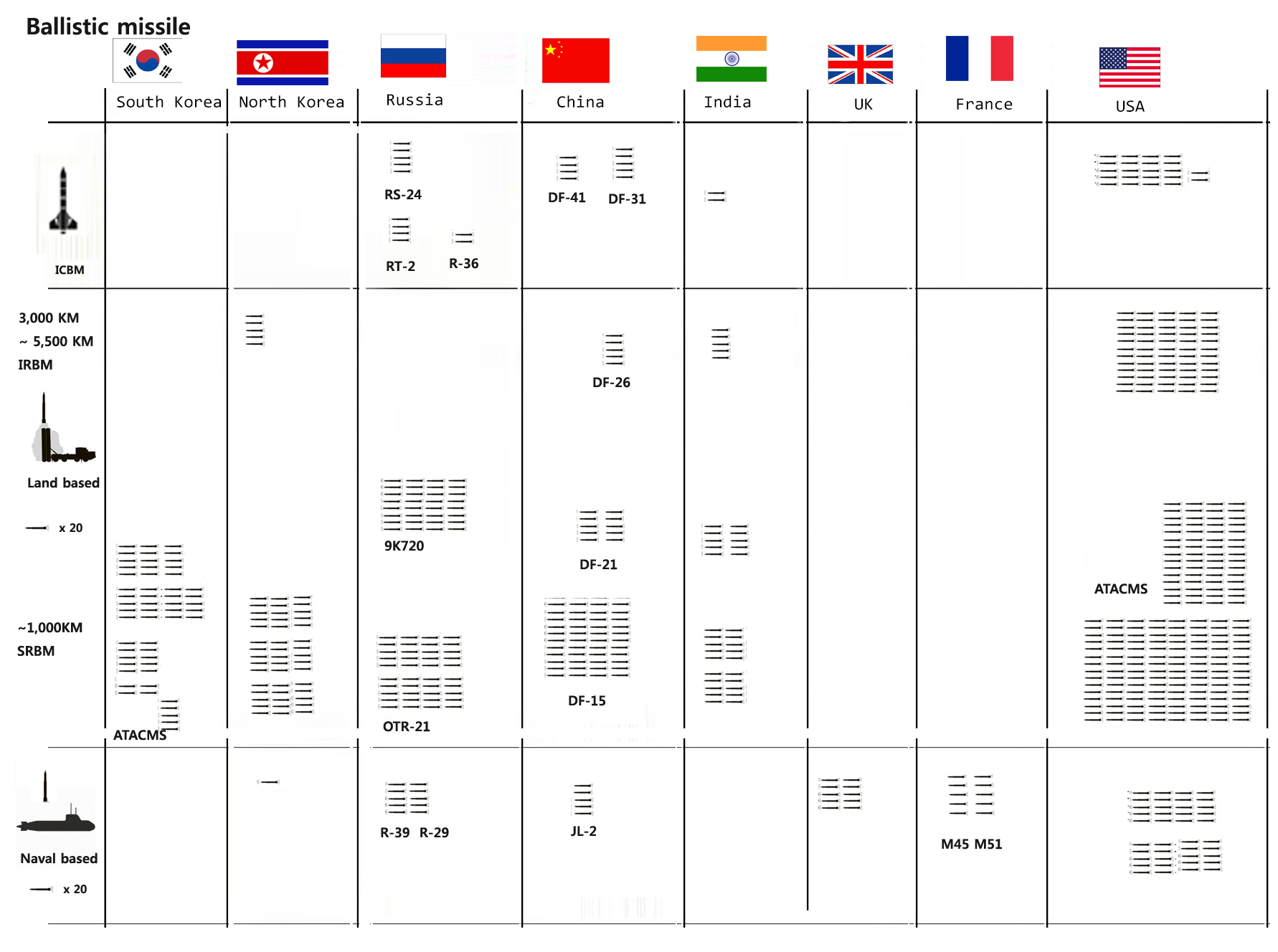
For this particular advantage, longer range missiles like Intercontinental Ballistic Missile (ICBM) operates using ballistic missile technology. Figure 3 represents the country-wise ballistic missile inventory.
Missile Operation
Ballistic missiles delivers the payload to a specific target using a primary boost phase followed by an unpowered flight at the terminal stage. The core operational difference between a cruise missile and a ballistic missile is the terminal propulsion mechanism.
A cruise missile is propelled with jet engines during the whole flight trajectory whereas ballistic missiles experience unpowered flight during the end-course period. A ballistic missile operation can be described as followed:
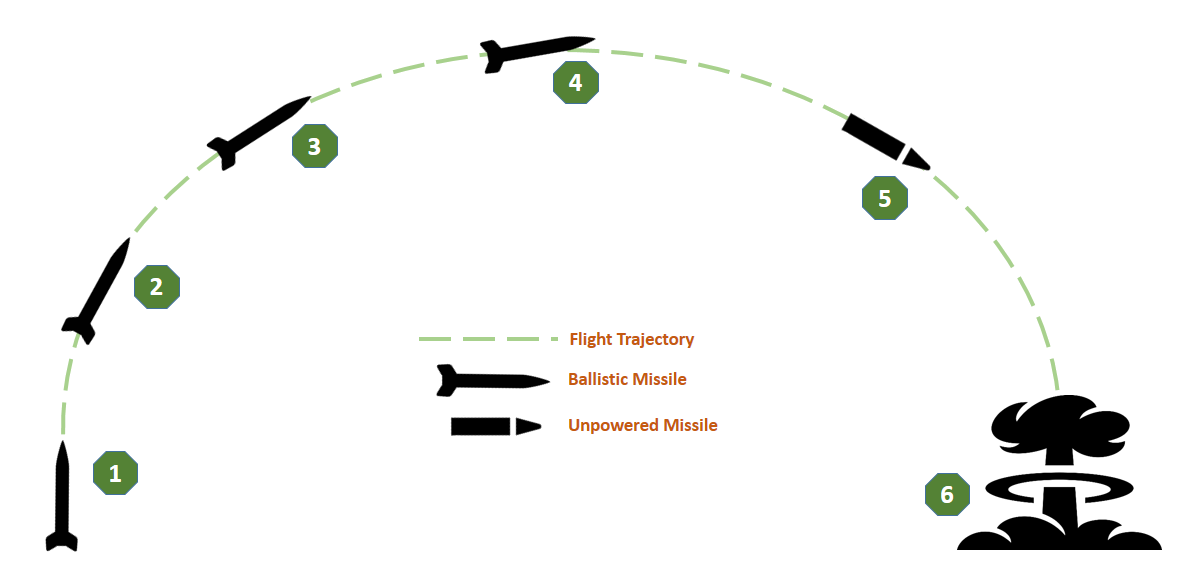
Figure 4: Ballistic missile operation, credit: author.

The missile is launched from the launching facility. At this stage, the missile is powered by the first stage boost engine. This engine generates the required thrust for the initial flight. The control & guidance system of the missile is also activated during this phase.

At 2nd stage, the first stage boost engine separates from the missile and the 2nd stage engine starts to propel the missile. 2nd stage of missile operation terminates while the 2nd engine burns out the whole fuel and separates from the missile.

This phase begins just after the separation of 2nd stage engine. The final jet engine ignites and the guidance system of the missile helps it to propel towards the mid-point of the ballistic trajectory. For most of the long range ballistic missiles, the 3rd stage also includes hovering out of the earth’s atmospheric level.

The 4th stage is about reaching the mid-point of trajectory and then initiating the flight back towards the atmosphere. The final jet engine separates from the missile after reaching the mid-point. The missile then starts to follow the predetermined flight path without any thrust generators.

This stage of missile operation is about re-entering the earth’s atmosphere. The unpowered ballistic missile then only carry the warhead that contains the payload. Some long range missiles carries a secondary control mechanism that helps to track and engage with the target precisely. Small thrusters are often attached along with the warhead to increase the accuracy of the engagement.

The missile finally engage with the target and explode. The explosion radius and the aftermath depends on the payload and their types. Nuclear warheads creates massive hazard while biological and chemical warheads does lethal damage to the target area.
Missile Classification
Ballistic missiles are mostly used in long range operation. The categorization of ballistic missile is also dependent on the operational range of the missile. Different military agencies use different standards to classify ballistic missiles. The US standard categorization of ballistic missile is discussed here:
Short Range Ballistic Missile

Missile with the operational range about 1000 kilometers or lesser than that are classified as short range ballistic missiles (SRBMs).
For quick and short ranged operations, SRBMs are well favored by the military agencies across the globe.
Comparatively reduced fuel consumption with better speed provides SRBMs more flexibility than cruise missiles.
SRMBs are mostly used to destroy enemy facilities from a safe distance in nearby camps. The US Army’s MGM Lance, Russian Iskander and Tochka are the examples of short range ballistic missiles.
Medium Range Ballistic Missile

Medium range ballistic missiles (MRBMs) have the operation range from 1000 kilometers to 3000 kilometers.
These missiles are used in lethal operations in a warzone.
The modern military agencies often categorize SRBMs & MRBMs into a broader class named Theatre ballistic missile (TBM). MRBMs are useful against a moving target within a medium range from the safe house.
Iran, North Korea and Pakistan are the countries that mostly use MRBMs at present times.
Intermediate Range Ballistic Missile

Missiles having the operational range of 3000 to 5500 kilometers are classified as Intermediate Range Ballistic Missiles (IRBMs).
The history of IRBMs dates back from the World War II while the German military used A4b rockets widely both in manned and unmanned air strike. China, India, North Korea still use the IRBMs while USA, France and UK no longer conducts IRBM operations.
Intercontinental Ballistic Missile

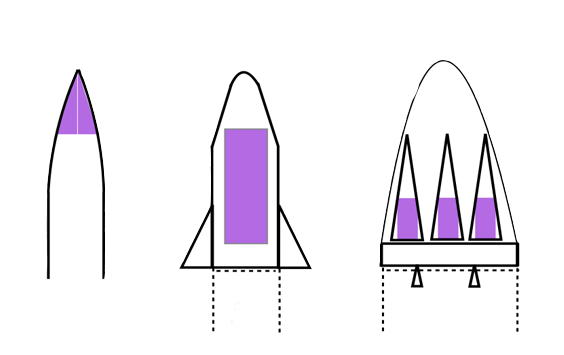
Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles (ICBMs) are very long ranged self-propelled ballistic missiles.
These missiles can engage a target with more than 10000 kilometer operational range. ICBMs are initially launched from ground based launching facilities and travels to the earth’s orbit into the outer space and then reenter the atmosphere with an enormous velocity.
The minimum range of an ICBM is set to be 5500 kilometers and the maximum range varied from 7000 to 16000 kilometers. R-36M of Russia is currently the longest ranged missile in the world with an operational range of 16000 kilometers. ICBMs are capable of carrying larger payloads to a very long distance with comparatively improved accuracy.
The warhead of an ICBM can carry multiple payloads as shown in the Figure 9.
By the time missile leaves the earth’s atmosphere and travel within the space, the maximum speed of the missile can reach almost 27,360 km/hr.
Though countries can conduct ICBM operations over continents but till date no ICBMs were fired to engage with an enemy in wars across the globe. The video below shows the launch of US Navy’s Trident II ICBM from a submarine in the Atlantic Ocean.
Again the Russian military classified ballistic missiles into five following categories.
| Missile Type | Range (km) |
| Tactical | up to 50 |
| Operational-Tactical | 50 to 300 |
| Operational | 300 to 500 |
| Operational-Strategic | 500 to 1000 |
| Strategic | over 1000 |
Conclusion
Missiles are widely used by modern military agencies since the WW2 because of the effectiveness against enemy air defense.
Missiles can be used in both defensive and offensive operation against the threat network across the globe. Having the advantage of minimal maintenance and training support, missiles are being favored since decades.
These are capable of operating in high accuracy with adequate risk of friendly casualty.
With the advancement of military science, missile technology is proving to be more practical and safe option than manned operations.
The longer operational range along with the improved speed make the ballistic missiles useful in war combats.
ballistic missiles are launched towards the highest layers of the atmosphere that allows them to travel a much longer distance compared to the cruise missiles.
Additionally the terminal phase of the ballistic missiles are unpowered that allows it to operate almost half of its trajectory without any fuel consumption.
These operational advantages make ballistic missiles one of the most used weapon of mass destruction by the military agencies all over the world. Moreover, ballistic missile defense system is introduced by the most advanced military agencies in recent times.
The defense system intercepts with the incoming missile with a target seeking missile launched from ground based facilities.
The defensive missile engage with the income threat in mid-air and cause the missile to explode before entering the earth’s atmosphere.
That’s the much we can take on the topic “Missile Technology – The Weapon Of Destruction”.
Thanks For Reading
Leave a Reply